First Metacarpal
What is the First Metacarpal Bone
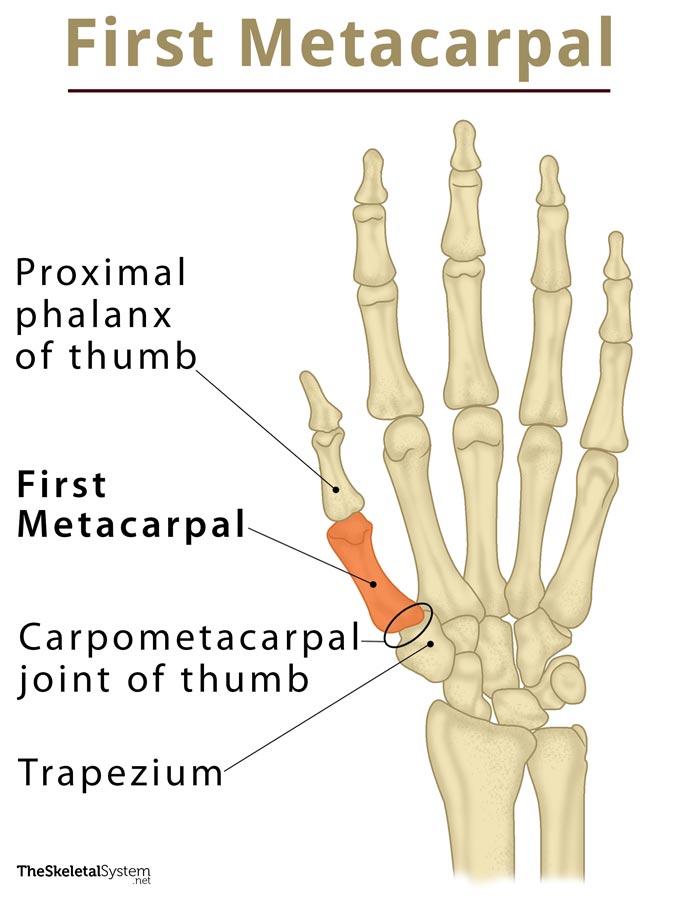
The first metacarpal (1st Metacarpal) is the metacarpal or palm bone associated with the thumb and is the shortest, and most mobile of all the five metacarpal bones [1].
Where is it Located
Being the metacarpal of the thumb, it is located distally on the radial side of the human palm, between the distal carpal row, and the first proximal phalanx [12].
Development and Ossification
The first metacarpal starts to ossify from two centers, the first for the body or shaft, and another for its base [11]. This shows that this metacarpal ossifies in a similar manner as a phalanx. This observation led some anatomists to suggest that the thumb actually has three phalanges instead of two phalanges and a metacarpal [10].
The ossification centers for the shafts for all metacarpals start appearing around the 8th or 9th week of fetal growth, with that of the first metacarpal appearing last. Its base begins to ossify when the child is about 3 years old [9].
Anatomy of the Metacarpal of Thumb
Surfaces and Joints
On its head, it articulates with the proximal phalanx of the thumb [1] to form the first metacarpophalangeal joint, while the base of the first metacarpal articulates with the carpal bone trapezium to form the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb or the trapeziometacarpal joint (TMJ) [2].
Carpometacarpal Joint (CMC Joint) of the Thumb
The CMC joint of the thumb is of fundamental importance in structuring the hand in humans and other primates, allowing the use of the thumb to hold objects [3]. The articulation between the first metacarpal and trapezium forms a saddle joint [2]. It is a type of synovial joint where the trapezium forms a concave or saddle-shaped articular facet for the base of the first metacarpal so the latter can sit into the space like a rider on horseback [4]. As a result, the metacarpal of the thumb makes almost a right angle to the metacarpals of the other digits, allowing it to rotate and move in nearly all directions [5].
Muscle Attachments
There are three muscles attaching to the first metacarpal, namely, the abductor pollicis longus, opponens pollicis, and the first dorsal interosseous. Additionally, it is also partially the spot of origin for the flexor pollicis brevis, which primarily originates from the trapezium [6].
Common Injuries and Associated Conditions
Thumb Carpometacarpal Arthritis: Since over half of all functions of the hand involve the thumb, the first CMC joint is subjected to a lot of stress and pressure every day. As a result, it is the most common CMC joint, as well as thumb joint, to get arthritis [7]. Characteristic symptoms include pain and swelling around the base of the thumb, gradually radiating to the wrist, causing difficulty in any twisting movement like rotating a doorknob. Treatment may include exercise, anti-inflammatory medication, and surgery [3].
Fracture of the First Metacarpal: A fracture in this area can occur as a result of an accident or some sports injury, with the most serious type of fractures involving the carpometacarpal, and metacarpophalangeal joints of the thumb. The fractures may have specific names depending on their nature and location (e.g. the Bennett fracture at the base of the first metacarpal), with the treatment methods varying accordingly as well [8].
References
- https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-metacarpal-bones
- http://anatomyzone.com/anatomy-feed/first-metacarpal/
- https://www.jospt.org/doi/pdf/10.2519/jospt.2003.33.7.386
- http://www.innerbody.com/image_skel07/skel33.html
- https://ouhsc.edu/bserdac/dthompso/web/namics/firstcmc.htm
- https://books.google.co.in/books?id=96jG5n-vmPcC&pg=PA66&lpg=PA65&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false
- http://www.orthop.washington.edu/?q=patient-care/hand/thumb-arthritis.html
- https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/thumb-fractures/
- https://prohealthsys.com/central/anatomy/grays-anatomy/index-10/index-10-2/index-10-2/ossificationhand/
- https://www.bartleby.com/107/56.html
- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/metacarpal-bones-1
- https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/metacarpals