Flat Bones
What are Flat Bones
Flat bones are one of the types of bones found in the human body, classified based on their shape. As the name implies, these bones are flat, thin, and curved. They mainly help in the protection, production of blood cells, and body movement.
Examples of Flat Bones in the Body
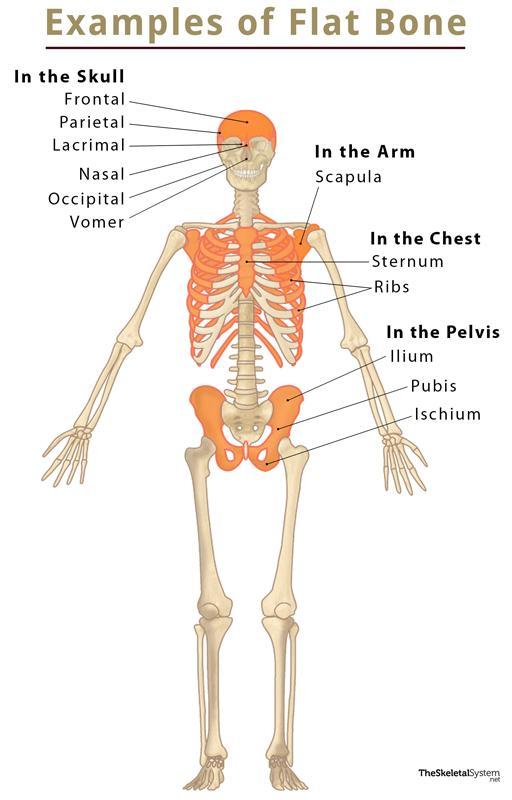
Skull Bones
- Frontal bone
- Parietal bone
- Occipital bone
- Nasal bone
- Lacrimal bone
- Vomer
Arm Bones
Chest Bones
- Sternum
- Ribs
Pelvic Bones
Functions
- Protecting various vital delicate internal organs — for example, the cranial bones protect the brain, the facial bones guard the eye and nose, the ribs protect the heart and lungs, and pelvic bones protect the reproductive and urinogenital organs.
- Acting as the attachment site for several important muscles, ligaments, and tendons, whose contraction and relaxation help in body movements
Anatomy
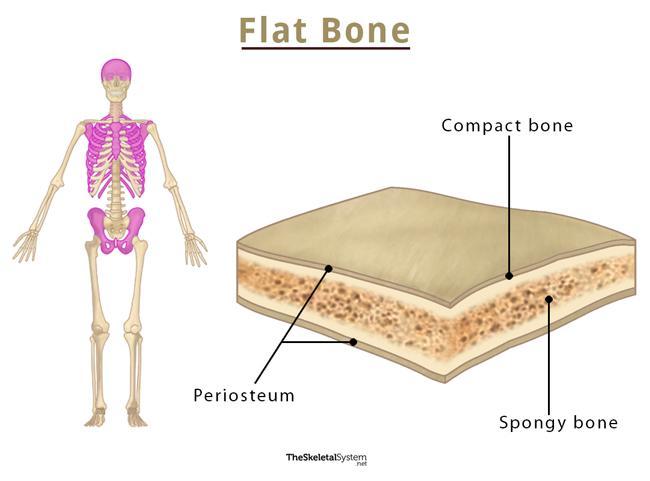
Flat bones are composed of a layer of spongy bone sandwiched between two thin layers of compact bone. These bones contain bone marrow but are devoid of any marrow cavity. Like any other bone, the periosteum covers the external surface of the bone.
Periosteum
As stated, this is the external membranous covering of the bone, containing blood vessels and nerves. These blood vessels nourish the bone by bringing nutrients to it.
Compact Bone
It forms the upper and lower outer layers of the bone, lying just below the periosteum. The compact bone is composed of very hard and dense bone tissue. Thus it strengthens the bone.
Spongy Bone
This innermost layer is lightweight and helps to absorb sudden mechanical shock. It is filled with red bone marrow, from where the red and white blood cells develop.
The flat bones in the skull share a characteristic feature. They articulate with each other, forming unique immovable joints called sutures. These joints do not fuse till a person is about 20 years old, allowing the brain to grow till then.
References
- Flat bones — Mountsinai.org
- Flat bones — Medlineplus.gov
- Flat Bones: Structure, Function and Examples — Study.com
- Classification of Bones — Training.seer.cancer.gov
- Flat bones — Ufhealth.org/flat-bones